Biochemical features of IVD degeneration
IVD is an outer AF, rich in collages accounting for its tensile strength, and inner nucleus pulposus (NP), containing large proteins that hold water to maintain the osmotic pressure required for resistance. per load. IVD (essentially healthy) is a normal vascular tissue and only the outer layer of AF is enhanced by sinuvertebral nerves containing sensory and post-toxic depression fibers.
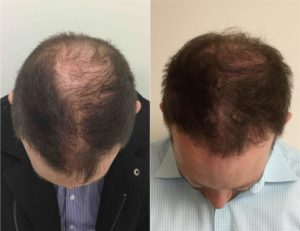
Click here : PRP Treatment Center in Lahore
While the precise mechanism for IVD decontamination is still unknown, it is known that the biochemical changes typical of the IVD declines include successive decreases of proteoglycan type and collagen content with subsequent dehydration and increased content of collagen type leading to tissue fibrosis. Importantly, pro-inflammatory cytokines, such as IL-1 and tumor-alpha necrosis (TNF-α), are thought to seriously affect matrix homeostasis during IVD degeneration by producing nitric oxide, metalloproteinases (MMPs), and encouraging aggregate, ultimately, the effluent matrix (ECM) of both the AF and NP tissues was eliminated.
In the disc degradation process, these inflammatory cytokines and molecules associated with inflammation, including neurotrophic factors, are considered responsible for discogenic LBP pathogenesis.
Neurotrophic factors have been shown to play a significant role in the transmission of physiological and pathological pain (see review. These include the neurotropic family known to have a role in inflammatory responses and transmission of pain through manifestation). peptides associated with pain increase in response to inflammation in local tissues.
The neurotrophin family (NT), including the nervous growth factor (NGF), the neurotrophic factor derived in the brain (BDNF), and NT-3 and its receptor, were also indicated in the IVD; these sentences are regulated in degraded and painful discs.27,28 These sentences of the NT family have shown that regulating inflammatory controls, such as IL-1β and TNF-α, are regulated. The NGF released in inflammatory IVD could act directly on nervous nerve fibers and sensory neurons to stimulate hyperalgesic effects. It is considered that the mutual interaction between inflammatory cytokines and the NT family plays a pivotal role in the discogenic LBP.
Definition of PRP and clinical application in orthopedic areas
PRP is an autologous blood concentration with a natural concentration of autologous growth factors and cytokines. PRP was widely used in the clinical setting for tissue regeneration and repair. Recently, particularly in the field of sports medicine and orthopedics, PRP has demonstrated regenerative capacity to repair injured tissues, including tendons, ligaments, and cartilage, all of which have low healing potential.
PRP was recently implemented in the treatment of Achilles and tendinopathies patein. The common injuries associated with sport often resonate with conservative medical management as it is an avian tissue with low healing potential. In their systemic review of the clinical effects of PRP injections on Achilles tendinopathy (12 papers) and patella tendinopathy (three papers reported that while few randomized control trials were carried out, most of the studies showed that the intrinsic injection of PRP pain and improved performance scores.
PRP was also applied for the treatment of osteoarthritis (OA). Recent meta-analysis of randomized randomized Level I tests (10 trials with a total of 1,069 patients) found that PRP injections were more effective for pain relief and functional improvement than injection of placebo (salt) and hyaluronic acid (HA). in the treatment of knee OA. Specifically, one study showed a significant improvement in pain and functional score than the placebo (salt) at post-injection 6 and 12 months and HA at post-injection 12 months. From the results of these clinical studies, the authors of the meta-analysis suggest that PRP is a promising treatment for cartilage injuries and mitigation of pain symptoms.
PRP biology and classification
The main function of platelets is to increase hemostasis by adhesion, activation, and the aggregation process. In response to vessel injury, platelets are activated and their granules release coagulation factors that create a fibrin clot. In addition to the factors that form blood, platelets were activated releasing growth factors. These growth factors increase inflammation and reassessment and accelerate epilepsy regeneration in the inflammatory and numerous stages of wound healing.
For more information visit our website PRP Treatment Center in Lahore